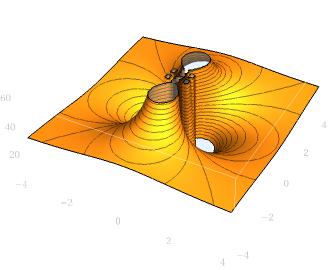
the Planck constants
The Planck constants define the boundaries of the coherent bases of atomic logic. Here we showcase their phase plots, 2D and 3D surface plots, and their closed-form definitions.
Phase plots
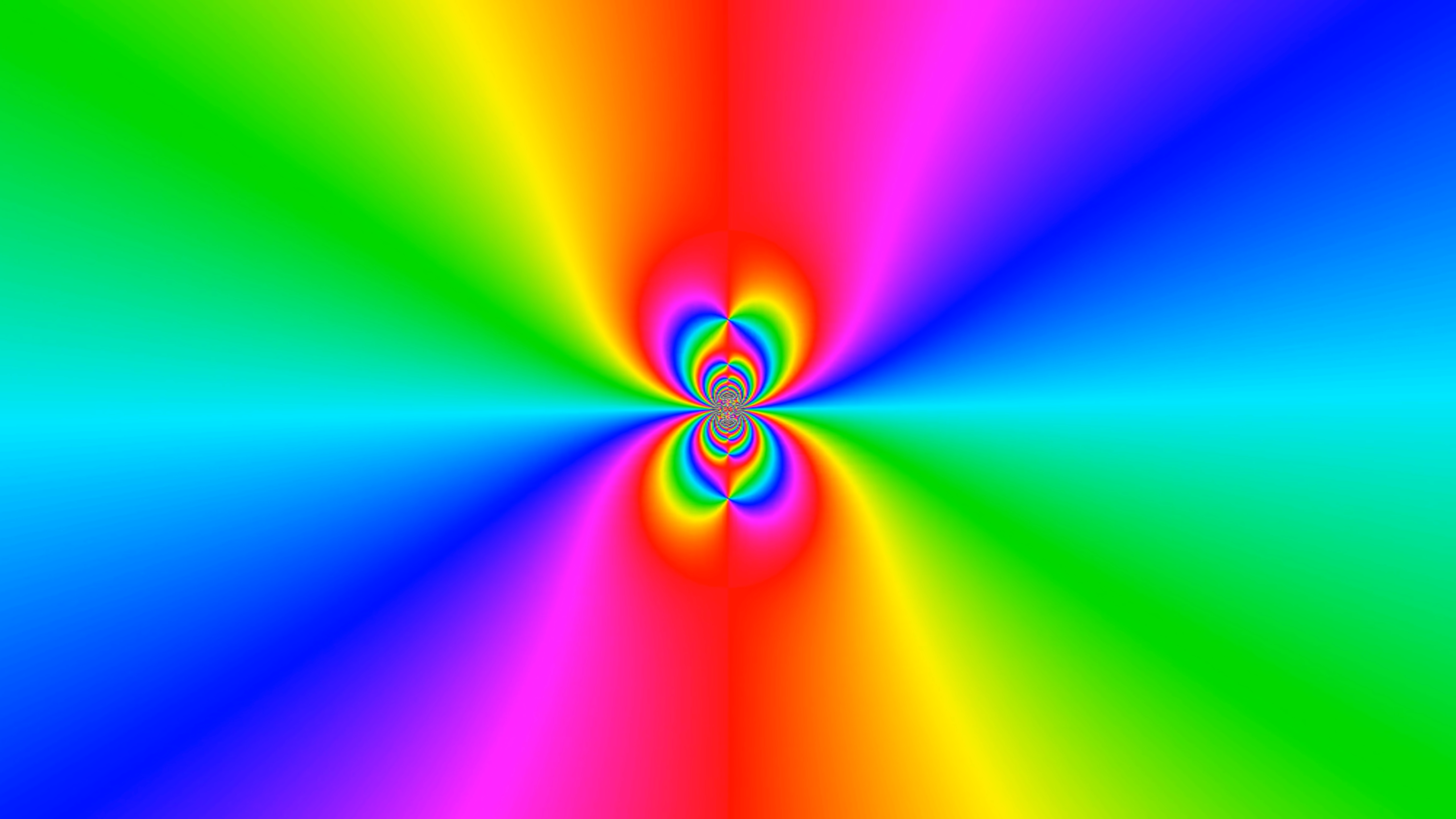

Planck time
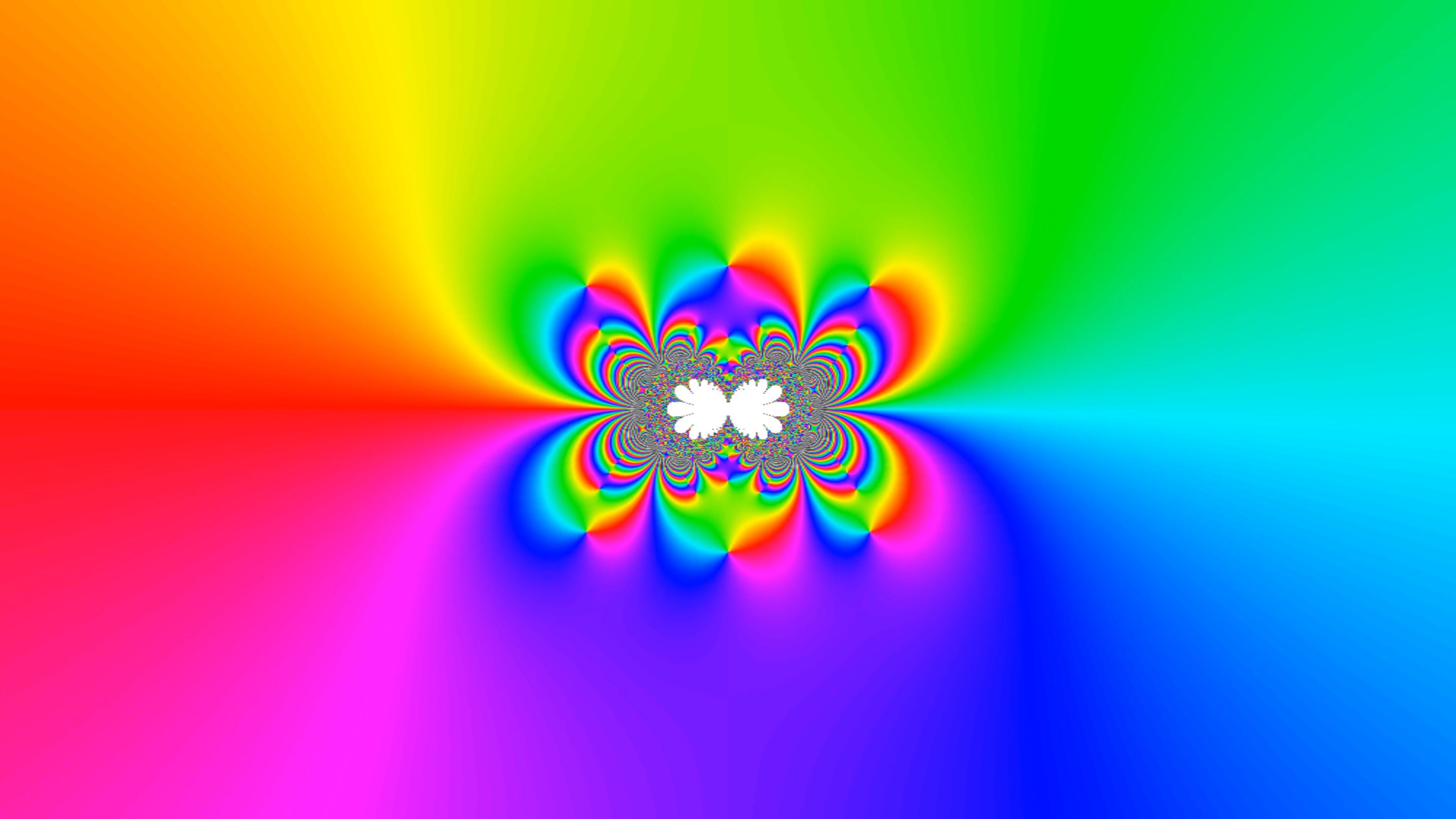

Planck length
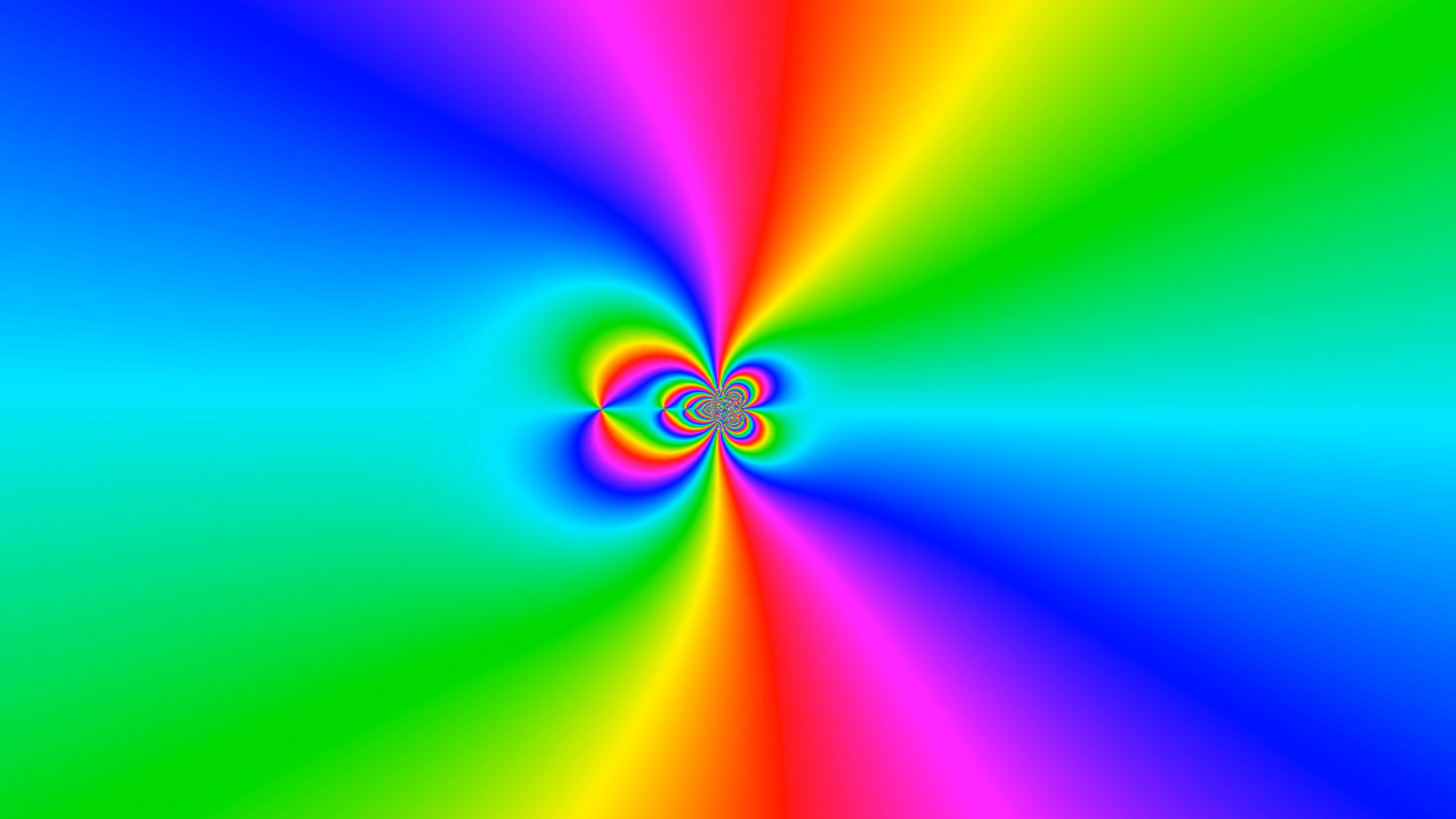

Planck charge
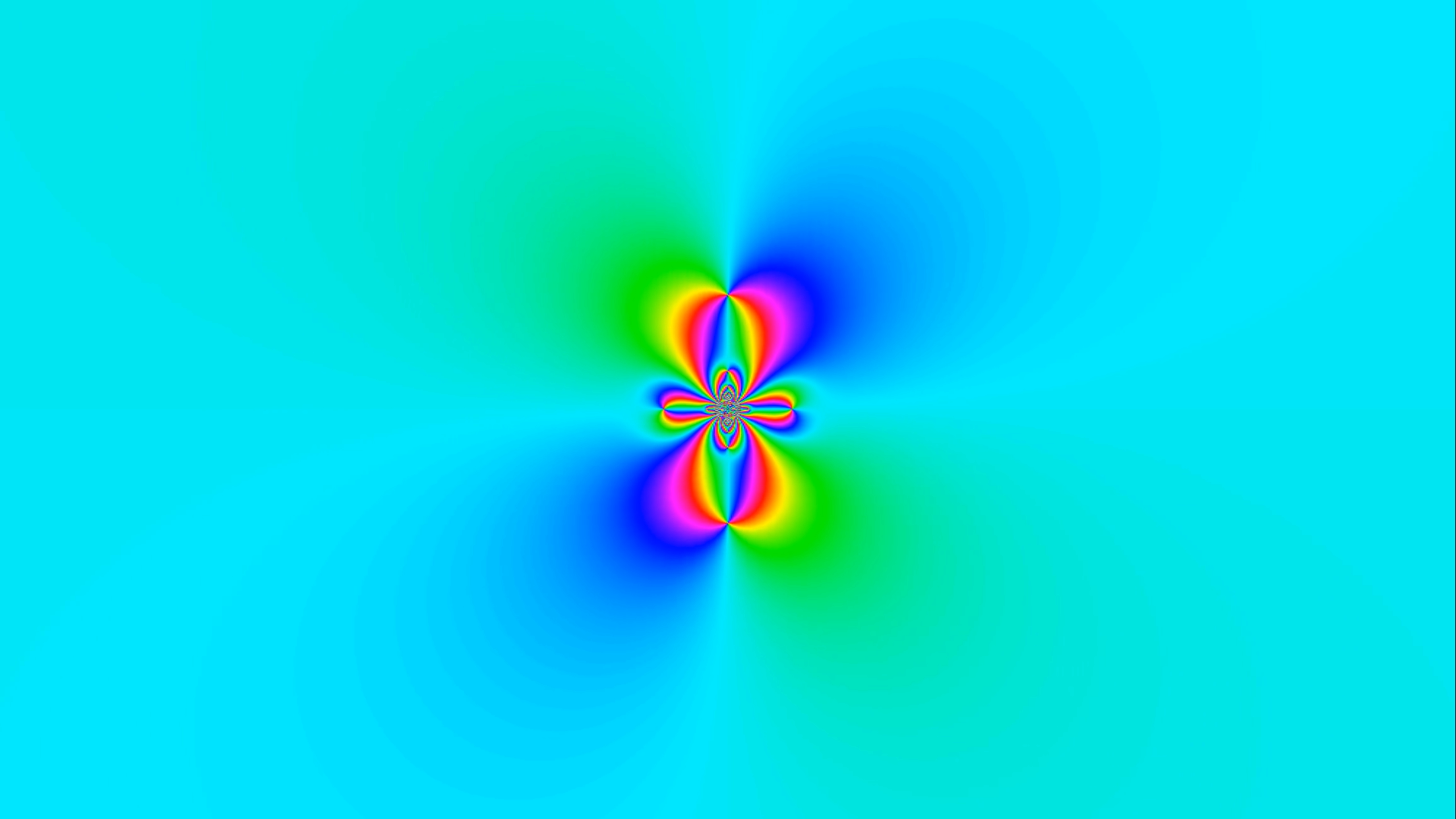
Planck temperature
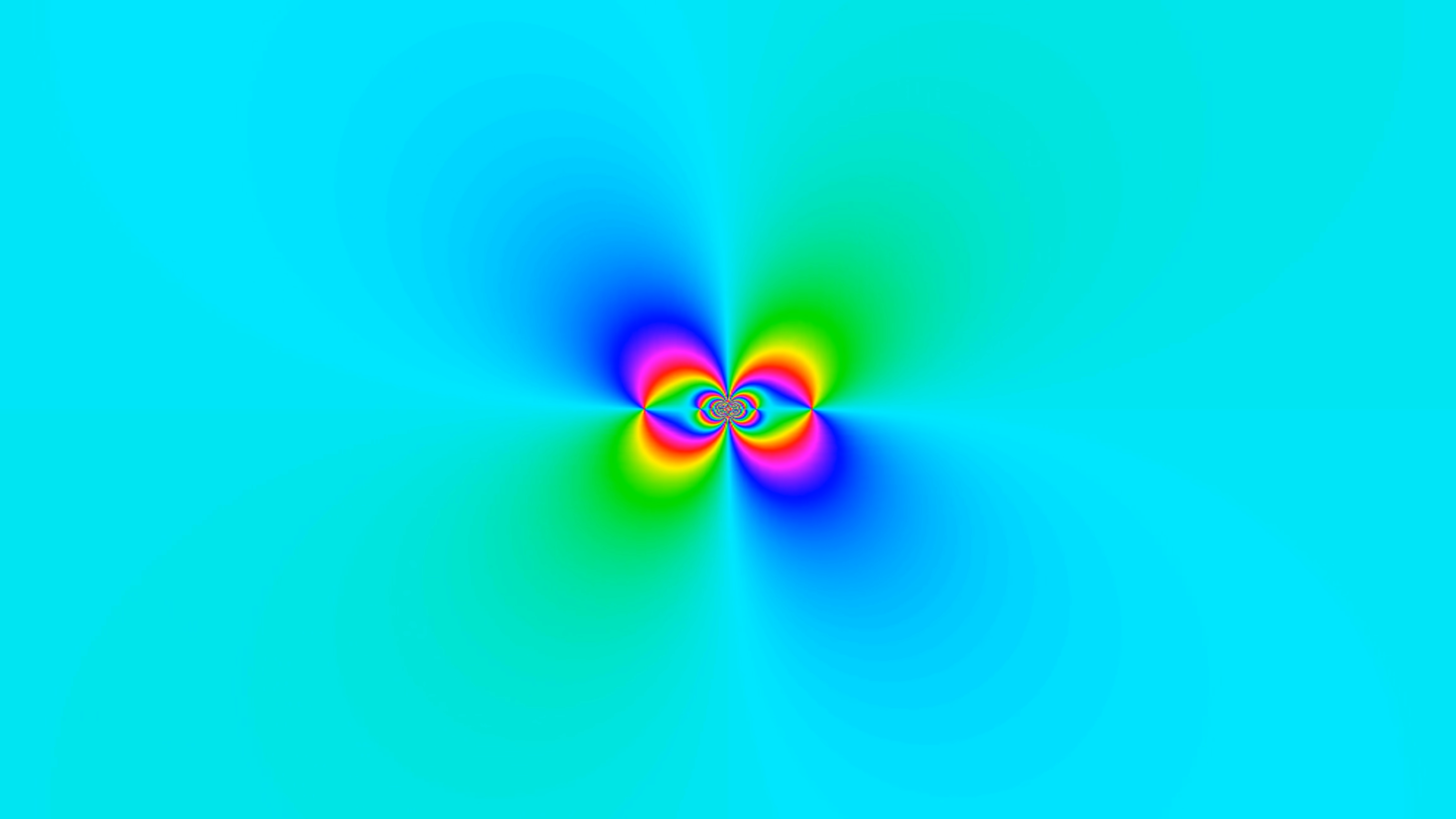

Planck mass
Surface plots
2D|3D
real|imaginary
Coherent closed-form definitions
Where = Archimedes' constant,
= the imaginary unit,
= Euler's number,
= the Weierstrass constant,
= the hyperbolic sine function, and
= the cosine function.
The decimal values of these closed forms yield numeric values for the Planck boundaries to any precision:
Planck time
Planck length
Planck charge
Planck temperature
Planck mass